Definition and overview
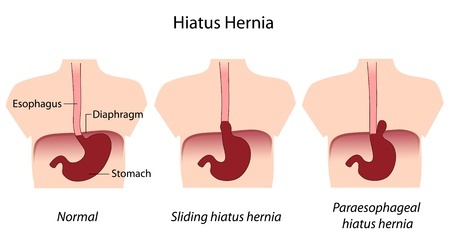
A paraesophageal hernia forms when more than one third of the stomach moves into the chest. The stomach pushes itself up through an opening that normally exists in the diaphragm, and through which the esophagus goes. There is a muscle located between the chest and the abdominal region that participates in the movements needed for an adequate breathing. When this muscle is too weak or the opening is too large, the stomach herniates (bulges) and places itself next to the esophagus. This abnormal displacement of the stomach may even cause it to twist around itself. The most common manifestation of this problem is the reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus, which can cause serious damage to it.
Laparoscopic paraesophageal hernia repair involves making small incisions in the patient’s abdomen, through which a tiny video camera and some surgical instruments will be inserted. The surgeon then gets a clear view of the patient’s abdomen and can perform a repair with minimum invasion. This repair may involve a strengthening of the diaphragm or a reduction of the opening’s size, depending on what’s causing the hernia.
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
Undergoing laparoscopic paraesophageal hernia repair brings tremendous benefits to the patients. Without treatment, the herniated tissues can be trapped in the chest – a very complex situation that can put the blood flow to those tissues in danger. This can cause severe chest pain and problems swallowing, which eventually progress to more serious medical issues. With laparoscopic repair, the symptoms of the hernia may be relived and further damages prevented.Because it’s a minimally invasive procedure, hospitalization times are shorter, pain is smaller, scars are negligible and recovery is relatively fast.
The disadvantages associated with this procedure are not numerous and are mostly related to its inherent risks. These are listed below.
Reasons for the procedure
Small paraesophageal hernias can generally be managed with the help of certain medications, namely those that control acid reflux (e.g. proton pump inhibitors, like omeprazole). On the other hand, patients with bigger hernias, certain types of hernias, severe damage to the esophageal surface caused by the stomach acid are eligible for the surgical repair. Same applies to the patients whose symptoms (which can include vomiting, trouble swallowing food, chest pain and pulmonary dysfunction) does not improve with drugs.
Risks of the procedure
Some of the problems that can happen in the course of the laparoscopic paraesophageal hernia repair are:
- Injury to the esophagus, stomach or surrounding nerves or blood vessels
- Infection
- Excessive bleeding
- Blood clot formation
Contraindications for the procedure
Although a laparoscopic approach is preferred in most cases, there are certain circumstances under which the traditional technique might be advisable. For example, in the presence of infection, adhesions or variations in anatomy (such as deviations in the position of internal organs) the laparoscopic method might prove dangerous. In these cases the standard open surgery approach should be used.The procedure is also contraindicated to people with abdominal or mediastinal perforations, and its applicability should be carefully considered in people who have a history of these diseases.
Laparoscopic procedures are successfully used by the specialists of D.R.A Medical for the treatment of various conditions including paraesophageal hernia.