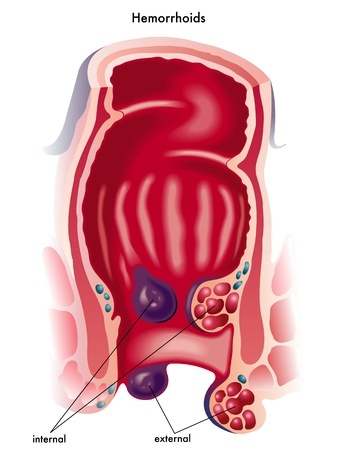
Overview
The walls of the rectum and the anus are composed of a set of muscles vital for their normal functioning. Located in these muscles, there is a group of blood vessels known as Hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids are a normal part of everyone’s anatomy and help control bowel movements. They only become a problem when they’re swollen and inflamed, which causes them to become painful for the patient. Under these circumstances, Hemorrhoids are also known as piles.There are two types of Hemorrhoids, according to their location. External Hemorrhoids are located under the skin around the anus and they constitute the most troublesome form of Hemorrhoids. Internal Hemorrhoids are located in the lower rectum, although they can protrude through the anus – a situation that can either revert naturally or stay prolapsed, thus requiring treatment.
Hemorrhoids affect mainly people aged 45 to 65 years old and they are quite common, since nearly 75% of all individuals will have Hemorrhoids at some point in their lives.

Symptoms
External and internal Hemorrhoids may have different signs and symptoms. Many people have a combination of both types.Internal Hemorrhoids are commonly identified upon the observation of bright red blood on stool, toilet paper or toilet bowl after a bowel movement. If the internal hemorrhoid has prolapsed, there can also be pain, itching and/or irritation and pain/discomfort in the anal region. In the event that the prolapse does not take place, the Hemorrhoids go unnoticed as they don’t usually cause discomfort.
External Hemorrhoids can present with thrombosis, following the formation of a blood clot. This may result in bleeding, pain, and the feeling of a sensitive lump near the anus.
In spite of these very uncomfortable symptoms, Hemorrhoids are generally not serious and they can go away without treatment. However, it is always important to visit a doctor in the presence of any of the symptoms, so that he can assess the severity of the condition and assign the best treatment.

Risk factors
Hemorrhoid swelling is thought to be caused by an increase in pressure, which leads to blood accumulation in the veins that compose the Hemorrhoids. The subsequent increase in size leads to symptoms. There are a number of factors that may increase the risk of the pathological changes of Hemorrhoids:
- Straining during bowel movements, something that may stem from maintaining a low fiber diet
- Pregnancy, due to an increased pressure of the distended uterus on the anus and rectum
- Acute and chronic diarrhea
- Colon cancer
- Obesity
- Prolonged sitting on the toilet
- Age, because the strength of the tissues surrounding the veins in the anus and rectum decreases as people get older
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Hemorrhoids normally involves a physical exam and the collection of the patient’s medical history. External Hemorrhoids are fairly simple to identify, especially if they blood clots have already formed.To evaluate the presence of internal abnormalities, the doctor may perform a digital rectal exam. If anything unusual is found, a sigmoidoscopy can be ordered. This technique involves using a small camera, the sigmoidoscope, to get a clear view of the rectum and therefore observe hemorrhoids in detail to properly evaluate them. If concerns regarding the presence of other conditions that are not Hemorrhoids are raised, a colonoscopy and a barium enema x-ray can be ordered.
Treatment
There are simple lifestyle modifications that anyone can do at home to reduce the swelling of Hemorrhoids and relieve the symptoms they cause. They include the increase of fiber intake and moderate exercise, both of which tend to improve the bowel movements. Defecation immediately when the urge arises prevents additional pressure and strain on the Hemorrhoids.
If the simple treatments do not help, there are some minimally invasive procedures that can be performed at the doctor’s office or outpatient hospital:
- Rubber band ligation - the doctor places a specific rubber band around the base of the Hemorrhoid, which cuts the circulation of blood to the Hemorrhoid, thus forcing it to shrink
- Sclerotherapy - a chemical substance is injected into the blood vessels, causing the Hemorrhoid to shrink
- Hemorrhoidectomy - through a small incision, the surgeon removes the Hemorrhoids and the surrounding blood vessels. This is usually a complication-free procedure that provides with a definitive solution for the problem.